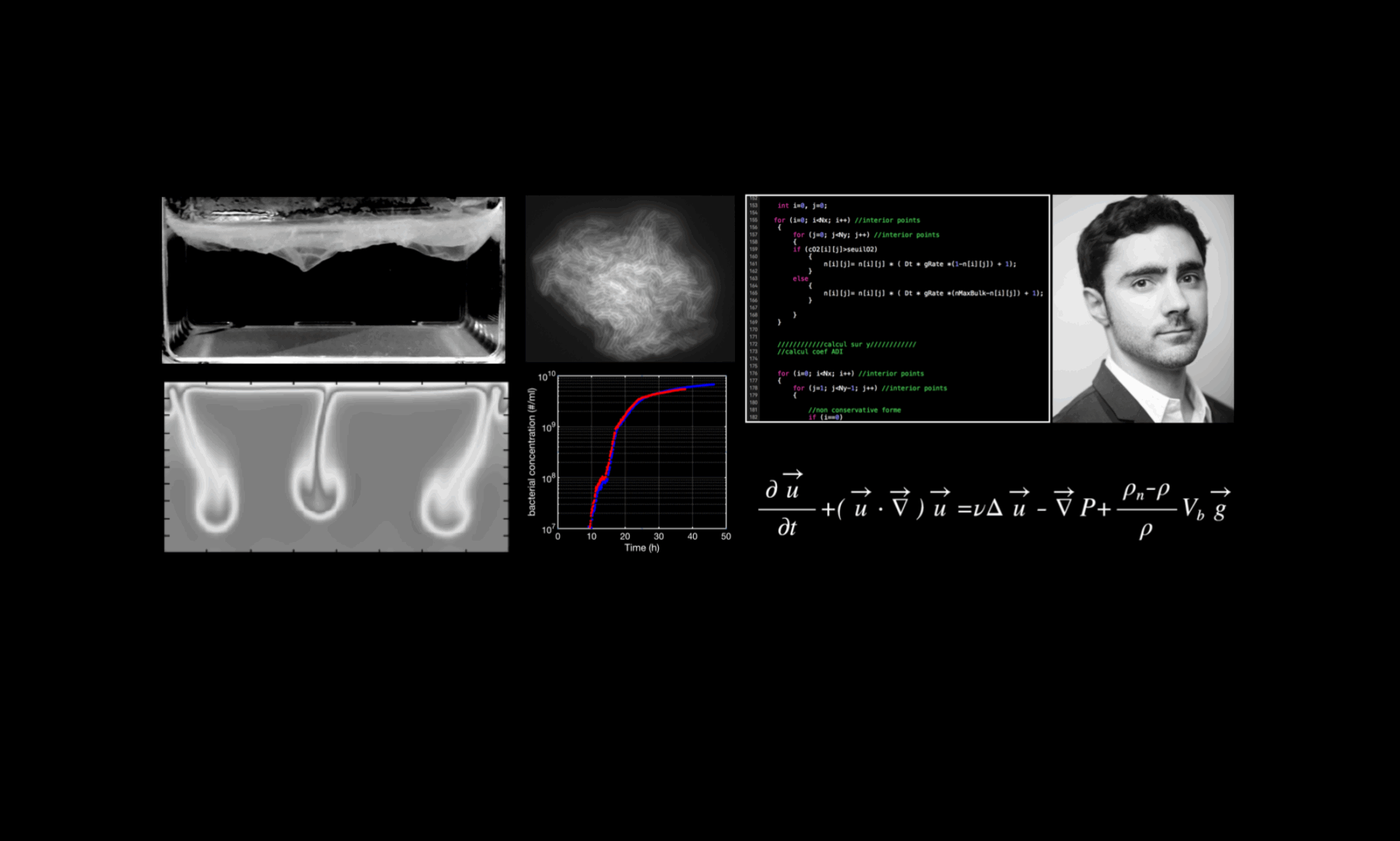
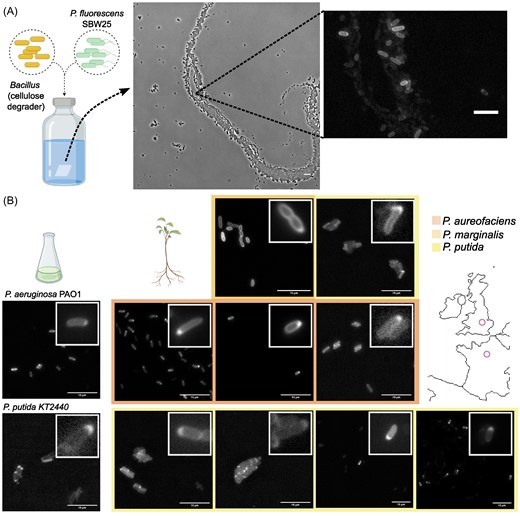
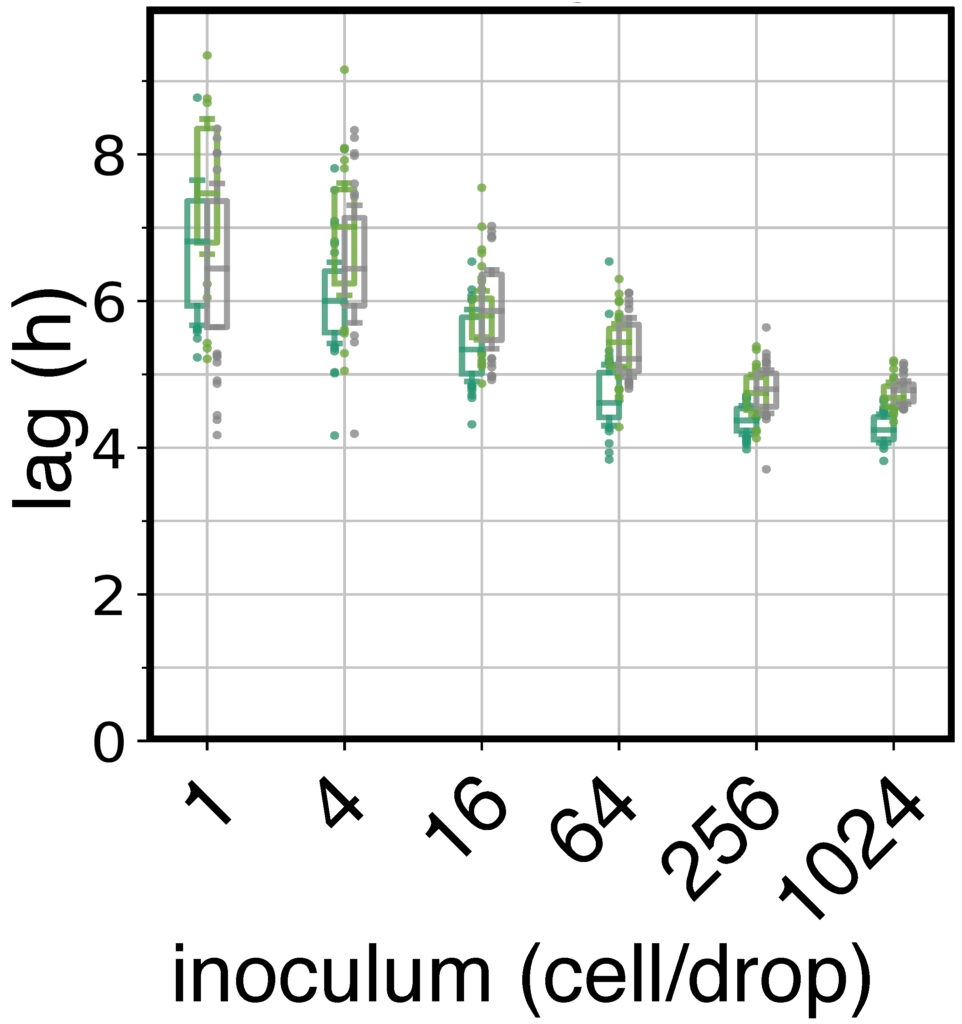
Bacteria make up the majority of life on Earth. They can be found everywhere: ocean, air, soil, animals, plants, etc. Their impact is monumental. For instance:
– in the soil, bacteria are stakeholders in the cycle of regeneration of agricultural land
– in the health, they are essential for the wellness of humans (intestinal flora, microbiota, skin barrier, etc)
– in the industry, they are used as a machine to synthesize drugs (insulin, antibiotics, etc.)
– in the medecine, they cause diseases
– on the environment, they incur the eutrophication of the oceans
– …
However, we are still scratching the surface of the bacteria significance. Some refer to them as the “dark matter alive”.
Major questions remain, such as:
– What kind of bacteria are living on Earth? (most of them do not grow in the laboratory of scientists to be easily indentify)
– What are the interplay between the bacteria and their environment?
– How do they interact with their neighbourhood?
– Do they communicate? If yes, how?
– Does bacterial population organize themselves?
– How do they adapt to their changing environment?
Thus, the stage is set for many important features to be explored and discovered.
The following is presenting research projects aiming at progressing toward the answer of these essential questions. Feel free to scroll down and have a look.